Copernicus: Powering Earth Observation with Sentinel Satellites
The Copernicus program, the European Union’s premier Earth observation initiative, delivers free, high-quality data to monitor our planet’s environment. Led by the European Commission and the European Space Agency (ESA), Copernicus uses its Sentinel satellites to provide insights into climate change, disaster response, and more. Let’s explore how Copernicus works and the specific ways its Sentinel satellites are transforming our world.
What is Copernicus?
Copernicus combines satellite and ground-based data to monitor Earth’s atmosphere, land, oceans, and ice. Its Sentinel satellites—each with specialized sensors—deliver near-real-time imagery and measurements, freely accessible through the Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem (https://dataspace.copernicus.eu). The program’s six core services—atmosphere, marine, land, climate change, emergency, and security—turn raw data into actionable insights for governments, businesses, and individuals.
How Copernicus Works
Copernicus operates through:
- Space Component: Sentinel satellites, including Sentinel-1, -2, -3, -5P, and -6, capture diverse data.
- In-Situ Component: Ground stations, buoys, and sensors provide local context.
- Service Component: Processes data into user-friendly products via the Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem.
Specific Uses of Sentinel Satellites
The Sentinel satellites power a wide range of applications. Here’s how each contributes:
Sentinel-1: Radar Imaging for All-Weather Monitoring
- Disaster Response: Sentinel-1’s radar penetrates clouds and darkness, mapping flood extents during events like the 2021 Germany floods. Emergency teams used its imagery to prioritize rescue operations within hours.
- Infrastructure Monitoring: Its data detects ground subsidence in cities like Jakarta, identifying sinking areas to guide urban planning and prevent building collapses.
- Agriculture: Farmers in Spain monitor soil moisture to optimize irrigation, reducing water waste in drought-prone regions.
Sentinel-2: High-Resolution Optical Imagery
- Precision Agriculture: In Brazil, Sentinel-2’s 10-meter resolution tracks crop health, detecting pest infestations in soybean fields early, boosting yields by up to 15%.
- Deforestation Tracking: Conservationists in the Amazon use Sentinel-2 to monitor illegal logging, alerting authorities to new clearings within days.
- Urban Planning: Cities like Copenhagen map green spaces to enhance urban cooling, using Sentinel-2 to assess vegetation coverage.
Sentinel-3: Ocean and Land Monitoring
- Marine Conservation: Sentinel-3 measures sea surface temperature, helping fisheries in the Mediterranean avoid overfishing by tracking fish migration patterns.
- Wildfire Management: In Australia, its thermal data monitors fire spread, guiding firefighting efforts during the 2023 bushfire season.
- Water Quality: Dutch authorities use Sentinel-3 to detect algal blooms in the North Sea, protecting tourism and aquaculture.
Sentinel-5P: Atmospheric Monitoring
- Air Quality: Sentinel-5P tracks nitrogen dioxide over cities like Delhi, informing policies that reduced urban smog by 10% in 2024.
Here’s a screenshot of the web interface where I was looking at a project focused on air quality emissions in New Delhi.
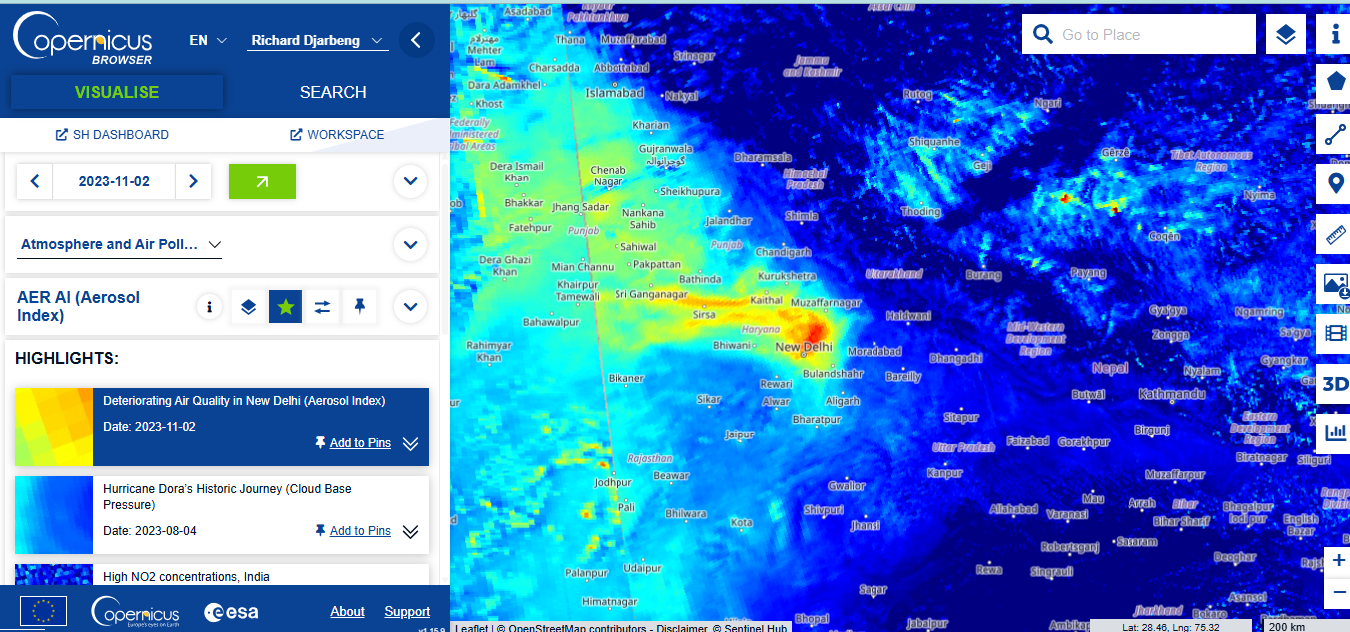
- Climate Research: It monitors methane leaks from oil fields in Texas, enabling targeted emission reductions.
- Volcanic Eruptions: During the 2022 Tonga eruption, Sentinel-5P tracked sulfur dioxide plumes, aiding aviation safety.
Sentinel-6: Sea Level Measurement
- Coastal Protection: Sentinel-6’s precise sea level data helps the Netherlands plan dike reinforcements, protecting low-lying areas from flooding.
- Climate Modeling: Its measurements of global sea level rise, increasing at 3.7 mm/year, refine IPCC climate projections.
- Storm Surge Prediction: In Bangladesh, Sentinel-6 data improves cyclone surge forecasts, saving lives through timely evacuations.
Support for Jupyter notebooks
It seems there is an option to use jupyter notebooks for those who wish to access the data through the familiar python notebook. Jupyter lab is now offered to copernicus users. Here’s a youtube video from the EU space youtube channel for a quick overview.
Why Copernicus Matters
Copernicus’ open-access model makes its data available to all, from scientists to startups. Through the Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, users access tools like the Copernicus Browser to explore imagery or APIs for custom applications. The program fosters global collaboration, sharing data with NASA and the UN to tackle pressing challenges.
Get Started with Copernicus
Ready to dive in?
- Explore Data: Visit https://dataspace.copernicus.eu to use the Copernicus Browser or download datasets.
- Learn More: Check success stories at https://www.copernicus.eu/en/use-cases.
- Get Support: Contact the Helpdesk at https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/support.
Copernicus is revolutionizing how we understand and protect Earth. Whether you’re tracking deforestation or planning a sustainable city, its Sentinel satellites provide the data to make a difference.